Please note: We are currently not accepting samples for in-situ hybridization.
The main function of our laboratory (UAZ-APL) is to diagnose diseases of cultured penaeid shrimp. Samples are received from farms and research facilities all over the world. We provide these diagnostic services through methods of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), Histopathology, and Microbiology. Diagnostic services are provided to the shrimp farming community and research institutions for a minimal fee. We are an accredited ISO/IEC 17025:2017 testing service provider - please see https://aquapath.cales.arizona.edu/accreditation for a detailed description of our accredited testing.
Sample Submission Guidelines and Form
Before you send samples, please take a look at our submission guide - it contains information on what sorts of samples we accept and how to ship them properly. Once you are ready to send your samples, please fill out and submit the sample submission form below, and send it with your samples. We cannot begin testing until we receive the sample submission form.
APL-Sample-Submission-Form-2025.docx
Pricing Information
Please see below for an up-to-date list of our prices for diagnostic testing. If you have any questions or would like to request a quote, please email acbs-aquapath-fin@arizona.edu
Import Permits
Looking to send our lab samples from outside the United States? Please include one of our import permits with your samples to ensure they do not get stopped at customs. There are two: one for sending crustacean tissues, and one for sending feed - please select the permit based on the samples you are sending. Each permit also contains more detailed information on what sort of samples they may be used for.
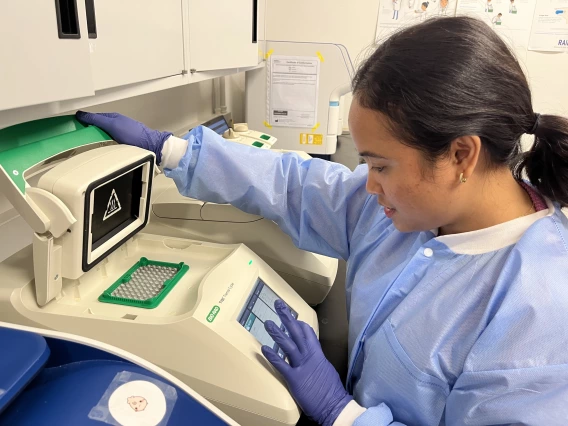

PCR
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) makes it possible to detect the "genetic fingerprint" of a pathogen by identifying and selectively amplifying unique nucleic acid sequences. This method is fast, relatively inexpensive, and highly sensitive—making it incredibly useful when screening organisms or their environment for specific pathogens.
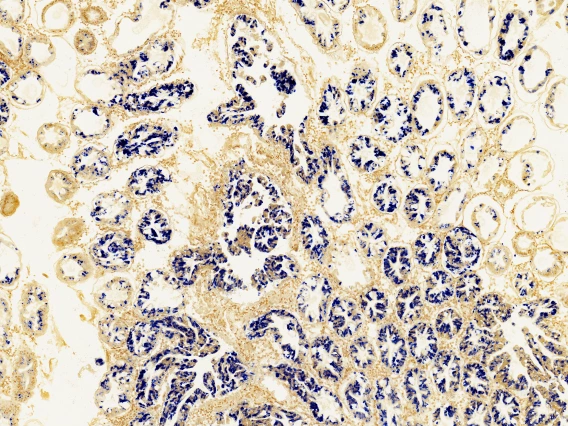
Histology
Histopathology allows visual examination at the microscopic level, after specimens undergo a series of processes that isolate, preserve, and highlight features of interest. Such examination of host organisms provides insight as to how (and if) a pathogen is causing damage.
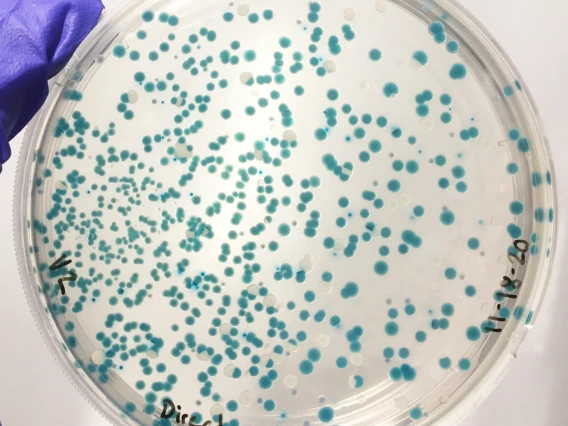
Microbiology
Microbiology combines visual observation and molecular biology to gain various information about potential pathogens. Traditional plating techniques are relatively inexpensive and can ascertain the extent of bacterial growth, and the relative abundancies of various metabolic processes. Molecular techniques are also often used to identify the species of unknown bacterial samples.

